Visual Attention Network
(작성중 10/27)
Abstract
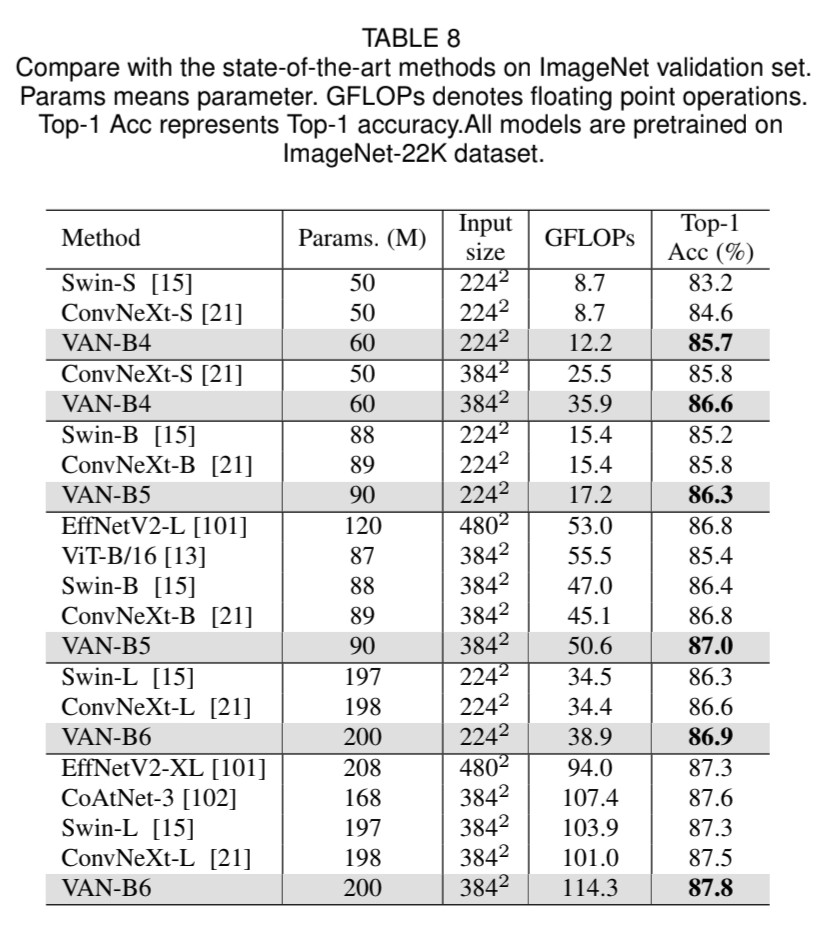
self-attention은 원래 NLP를 위해서 설계되었지만 폭풍처럼 Computer Vision에서도 최근 사용되고 있습니다. 그러나 self-attention을 computer vision에 사용하면 세 가지 challenge가 있게 됩니다. (1) Image를 1D sequence로 취급하는 것은 2D 구조를 무시하는 것이며, (2) 2차 복잡도는 고해상도 image에서 매우 비싸다는 문제, (3) channel adaptability를 무시하면서 spatial adaptability를 가지는 문제가 있습니다. 본 논문은 새로운 linear attention인 large kernel attention (LKA)를 사용하여 단점을 피하면서 self-attention에서 self-adaptive와 long-range 상관관계를 가능케 하였습니다. 추가로, 본 논문은 LKA 기반으로 한 neural network (Visual Attention Network(VAN))을 제안합니다. 극도로 간단하지만, VAN은 비슷한 크기의 vision transformers(ViT)보다 Convolutional Neural Network (CNNs)을 image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, panoptic segmentation, pose estimation의 다양한 task에서 성능이 좋습니다. 예를 들어, VAN-B6는 ImageNet benchmark에서 87.8%의 정확도를 달성하였습니다. Code는 https://github.com/Visual-Attention-Network에 있습니다.
Introduction
Computer Vision에서 AlexNet이 나오면서 deep learning 세계가 다시 펼쳐졌습니다. 더 깊은 신경망을 만드는 것이 유리해졌으며, 굉장히 powerful한 vision backbone이 만들어졌죠. 이후 NLP 분야에서 attention model, 특히 Transformer의 self-attention model이 나오면서 이 것을 vision 쪽에 사용하는 연구가 진행되었습니다. ViT (Vision Transformer)은 NLP에 사용했었던 Transformer을 Vision쪽에 사용한 model입니다. 이 ViT는 CNN보다 높은 성능을 보여주면서 Transformer 모델이 powerful한 모델이 됩니다.
기억할만한 성공에도, convolution operation과 self-attention은 단점이 있습니다. Convolution operation은 static weight를 가지고 있다는 점과 adaptability가 부족하다는 점입니다. 원래 1D NLP에서 사용되었던 self-attention을 사용하여 2D image를 1D sequence로 취급하는 것 또한 2D 구조인 image의 정보를 파괴할 수 있다는 점도 단점입니다. 게다가 고해상도 image에서는 2차 복잡도와 memory overhead를 가지고 있죠. self-attention은 spatial dimension에서 adaptability만을 고려하는 특별한 attention이지만, channel dimension에서의 adaptability는 무시합니다. 하지만 channel dimension의 adaptability는 visual task에서는 중요한 것이죠.
본 논문은 새로운 linear attention mechanism인, large kernel attention(LKA)를 제안합니다. LKA는 convolution과 self-attention의 local struction information, long-range dependence, 그리고 adaptability를 포함한 유익한 점을 이어갔습니다. 반면에, channel dimension에서의 adaptability를 무시하는 등의 안 좋은 점은 피하게 했습니다. LKA에 기반하여, 새로운 vision backbone인 Visual Attention Network (VAN)을 제안하며, 이는 잘 알려진 CNN-based와 transformer-based backbone을 능가하는 성능을 보여줍니다.
Method
Large Kernel Attention
Attention mechanism은 adaptive한 선택 과정으로 생각하면 됩니다. 즉, 차별적인 특징과 자동으로 input feature에 속한 noisy response를 무시하죠. attention mechanism의 주요 단계는 다른 부분의 중요성을 알려주는 attention map을 생산하는 단계입니다. 이러한 단계를 거쳐 다른 특징 간의 관계를 학습할 수 있습니다.
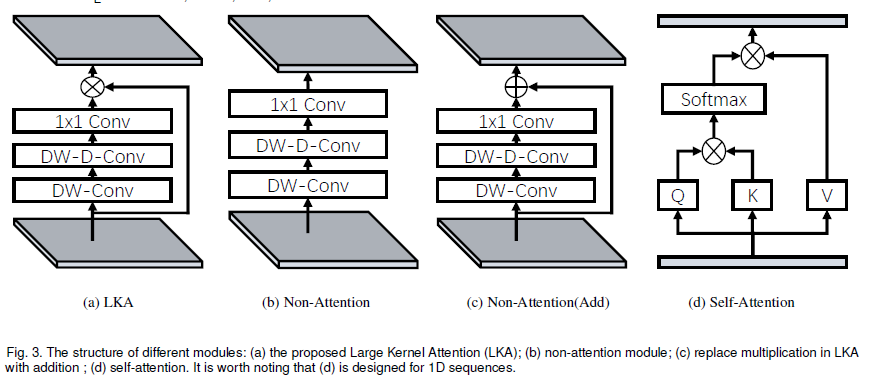
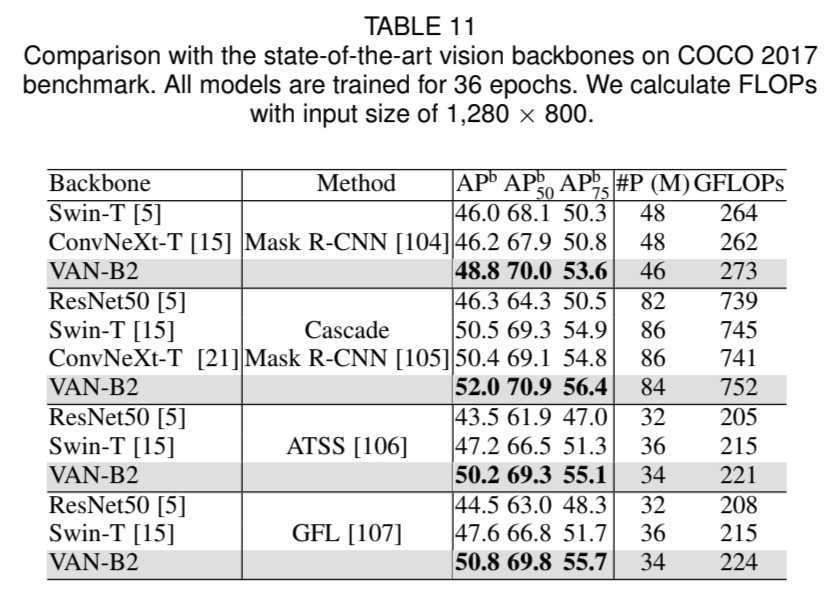
다른 부분과의 관계를 생성하는 잘 알려진 방법이 두 개 있습니다. 첫 번째로는 self-attention machanism을 사용하여 long-range dependence를 확보하는 것입니다. self-attention을 computer vision에 접목했을 때, 세 가지 단점에 대해서 언급했습니다. 두 번째 단점은 상관관계를 생성하고 attention map을 만들기 위해 large kernel convolution을 사용하는 것입니다. 여전히 여기에 분명히 단점이 있을 겁니다. Large-kernel convolution은 거대한 computational overhead와 parameter의 양을 초래합니다. self-attention과 large kernel convolution의 단점을 극복하고 장점을 사용하기 위해서는 long-range 관계를 얻기 위하여 large kernel convolution operation을 분리해야합니다. <fig 2>를 보면 large kernel convolution을 세 구성원으로 나눈 것을 볼 수 있습니다. : spatial local convolution (depth-wise convolution), spatial long-range convolution (depth-wise dilation convolution), 그리고 a channel convolution (1x1 convolution).
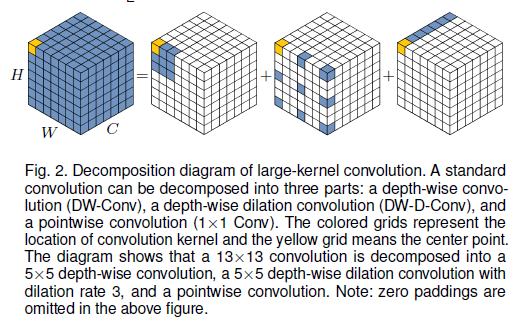
특별히, 본 논문은 $K\times K$ convolution을 $\lceil\frac{K}{d}\rceil\times\lceil\frac{K}{d}\rceil$의 depth-wise dilation convolution으로 분해하는데, $(2d-1)\times(2d-1)$ depth-wise convolution 그리고 $1\times1$으로 구성되어 있습니다. 위 분해과정을 거치면서, 가벼운 computational cost와 parameter를 가진 long-range relationship을 잡을 수 있습니다. long-range relationship을 얻은 후에, 본 논문은 point의 중요성을 평가하고 attention map을 생성합니다. <fig 3(a)>에 설명된 것 처럼, LKA 모듈은 아래처럼 쓸 수 있습니다.
$Output = Attention \otimes F$.
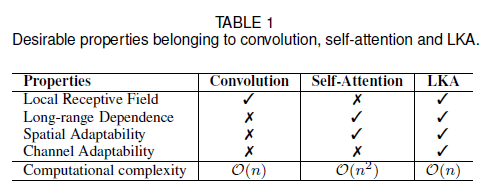
여기서, $F \in \mathbb{R}^{C\times H\times W}$는 input feature입니다. $Attention \in \mathbb{R}^{C\times H\times W}$는 attention map을 뜻합니다. attention map에 있는 값은 각 feature의 중요성을 가리킵니다. $\otimes$는 element-wise product을 뜻합니다. 흔한 attention 방법과는 달리, LKA는 sigmoid와 softmax와 같은 추가적인 normalization 함수가 필요하지 않습니다. 본 논문은 input feature을 기반으로 하여 output을 adaptively하게 조정하는 것이 attention 방법의 주요한 특징이라 생각합니다. <Table 1>에서 보면, LKA는 convolution과 sef-attention의 장점을 합하였습니다. LKA는 local contextual information, large receptive field, linear complexity 그리고 dynamic process를 고려합니다. 게다가, LKA는 spatial dimension에 있는 adaptability를 얻을 뿐만 아니라, channel dimension에 있는 adaptability도 얻을 수 있습니다. 다른 channel은 종종 deep neural network에서 서로 다른 객체를 나타내며, channel dimension에서의 adaptability 또한 시각적 작업에 중요합니다. 이것은 주목할만한 가치가 있습니다.
Visual Attention Network (VAN)
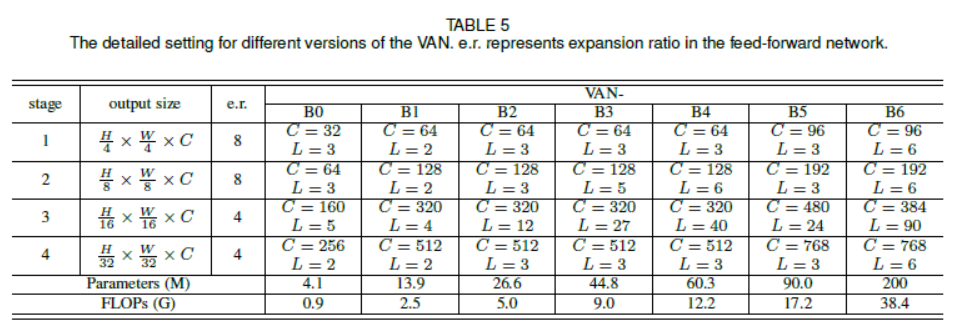
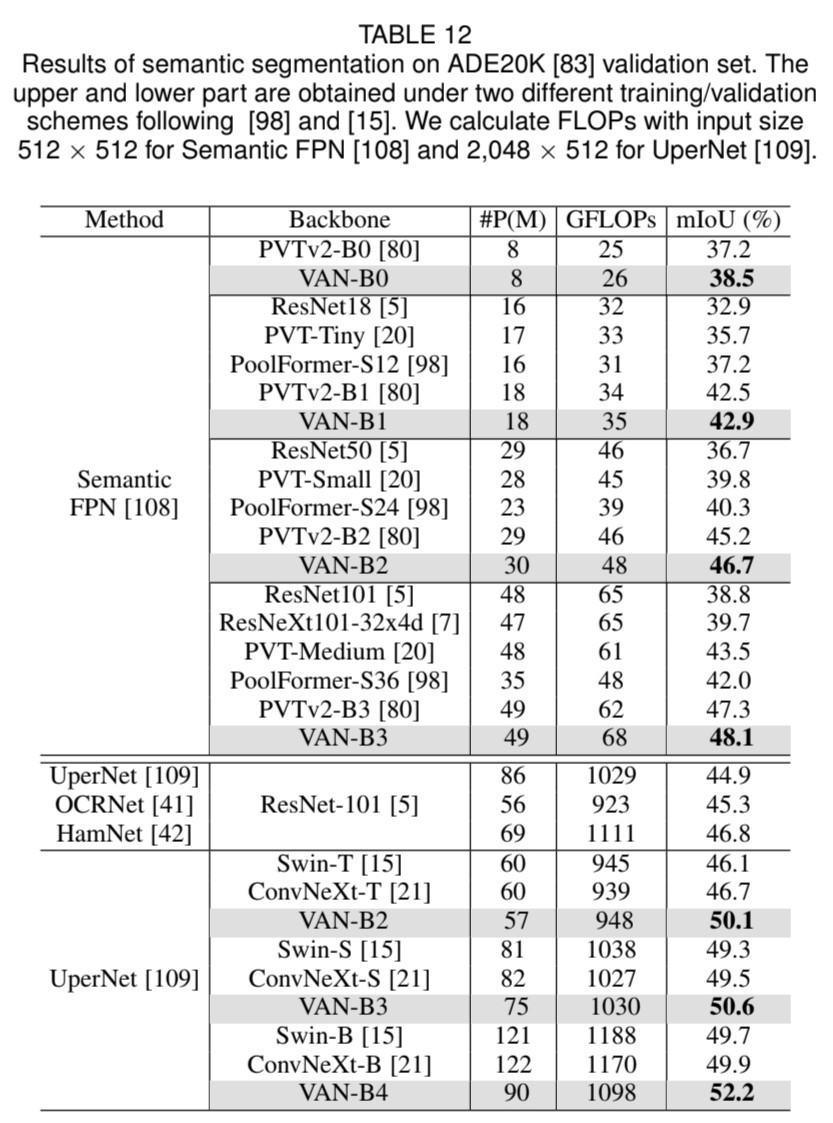
VAN은 간단한 계층적 구조를 가집니다. 감소하는 output spatial resolution을 가지는 네 개의 stage의 sequence로 되어 있습니다. 예를 들면 $\frac{H}{4}\times\frac{H}{4},\frac{H}{8}\times\frac{W}{8},\frac{H}{16}\times\frac{W}{16},\frac{H}{32}\times\frac{W}{32}$으로 되어 있습니다. 여기서, $H$와 $W$는 input image의 height와 width를 뜻합니다. resolution의 감소로 output channel의 수는 점차 증가합니다. output channel의 $C_i$의 변화는 <Table 5>에 있습니다.
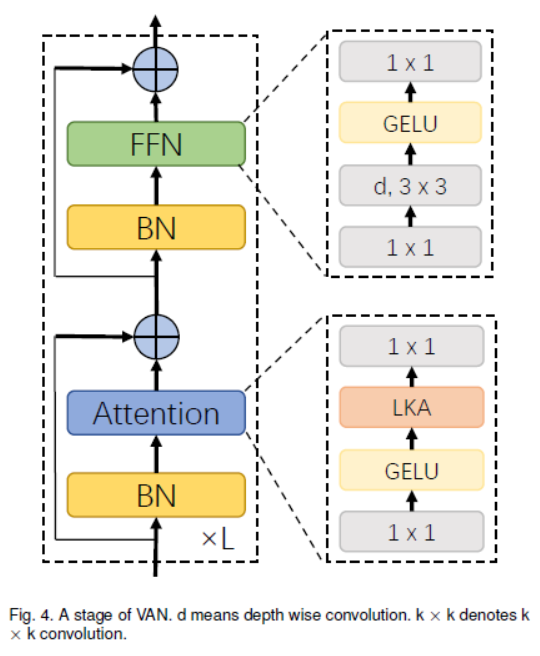
<fig 4>에서 각 stage를 볼 수 있습니다. 먼저 input을 downsample하고 stride number를 사용하여 downsample rate를 조절합니다. downsample 이후에도 stage 내의 다른 layer는 동일한 output size, 즉 spatial resolution와 channel 수를 유지합니다. 그 다음, batch normalization의 $L$ group, $1\times1$ Conv, GELU activation, large kernel attention 그리고 feed-forward network (FFN)이 sequence로 되어, feature을 추출합니다. 7개의 구조를 설계하였으며 이는 parameter과 computational cost에 기반합니다. VAN-B0, VAN-B1, VAN-B2, VAN-B3, VAN-B4, VAN-B5, VAN-B6. 상세한 내용은 <Table 5>에 있습니다.
Complexity analysis
- parmeter과 floating point operation (FLOPs)을 제시해보았습니다. Bias는 작기에 무시하였으며, input과 output feature이 $H\times W\times C$의 같은 크기를 같는다고 가정합니다. paramter $P(K,d)$의 수와 FLOPs $F(K,d)$는 아래와 같이 설명됩니다.
$F(K,d)=P(K,d)\times H\times W$. (4)
- 여기서, $d$는 dilation rate를 의미하며, $K$는 kernel 크기를 말합니다. FLOPs와 paramter의 공식에 따르면, 비용 절감의 비율은 FLOPs와 paramter에 같습니다.
Implementation details
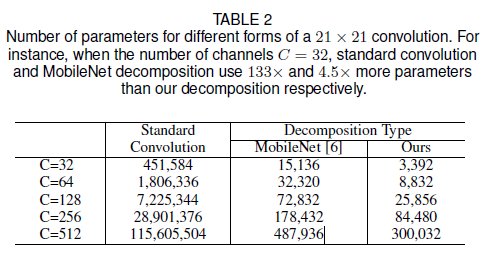
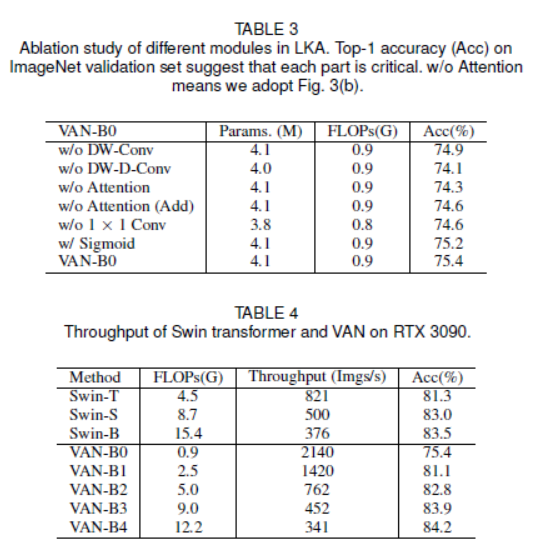
- $K=21$를 default로 설정하였습니다. 식 (3)에서 $K=21$이면 $d=3$일 때 최솟값을 가집니다. 이는 각각 $5\times5$ depth-wise convolution과 $7\times7$ depth-wise convolution에 각각 3의 dilation을 나타냅니다. 다른 channel에서, <Table 2>에서 parameter값을 보여줍니다. 이 표는, 본 논문의 구성이 large kernel convolution을 분해함으로써 parameter과 FLOPs 관점에서 엄청난 이익이 있음을 보여줍니다.
Experiments
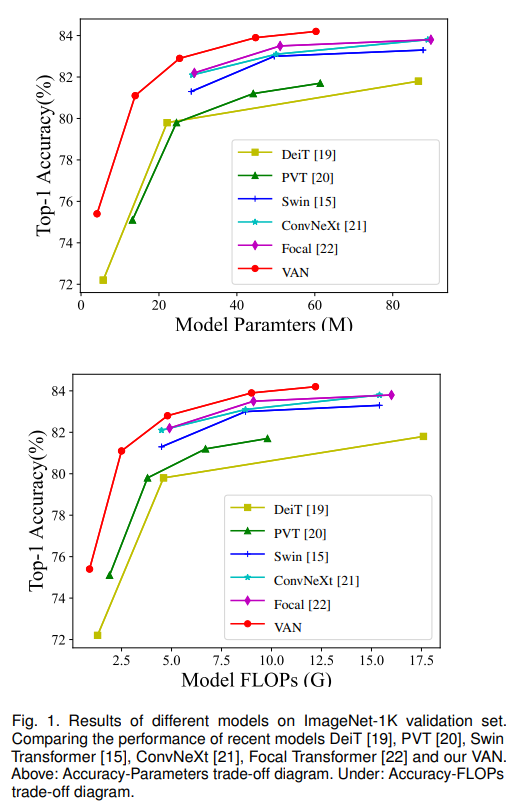
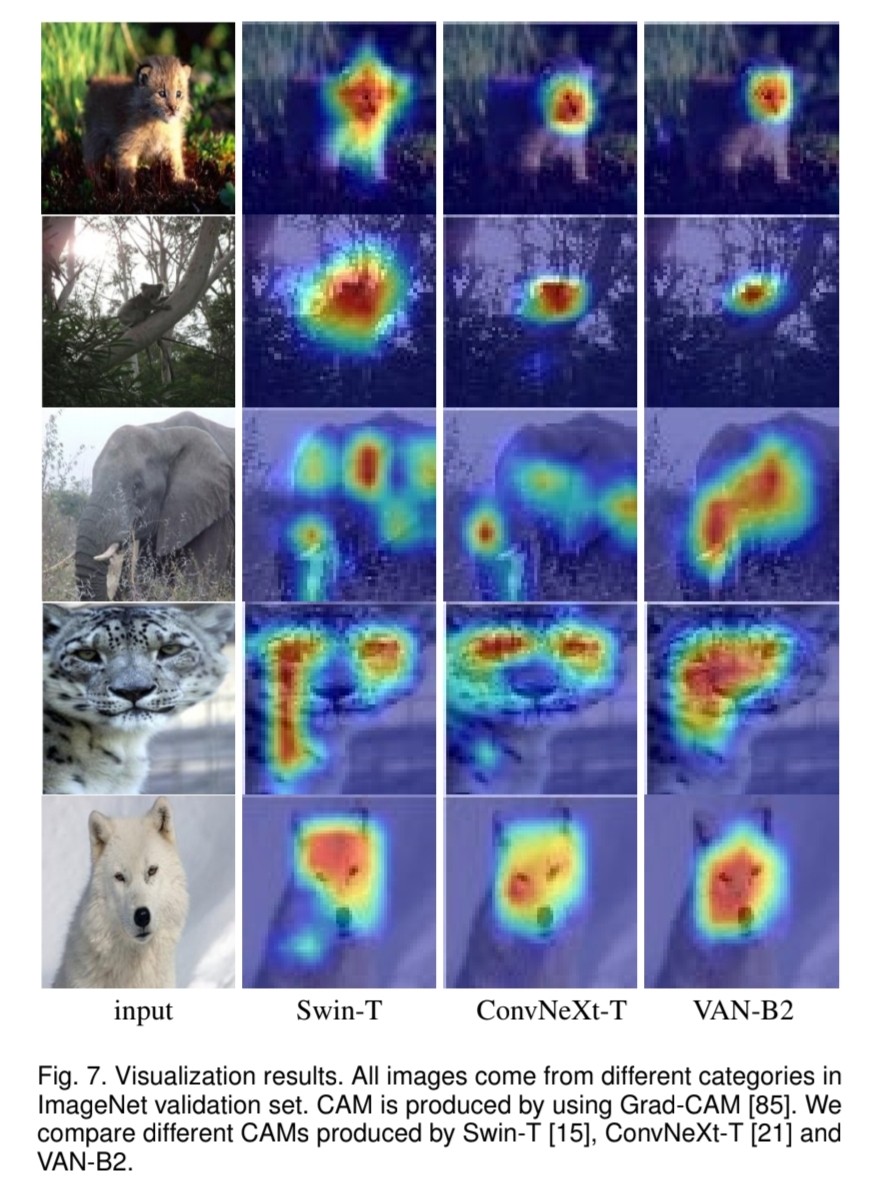
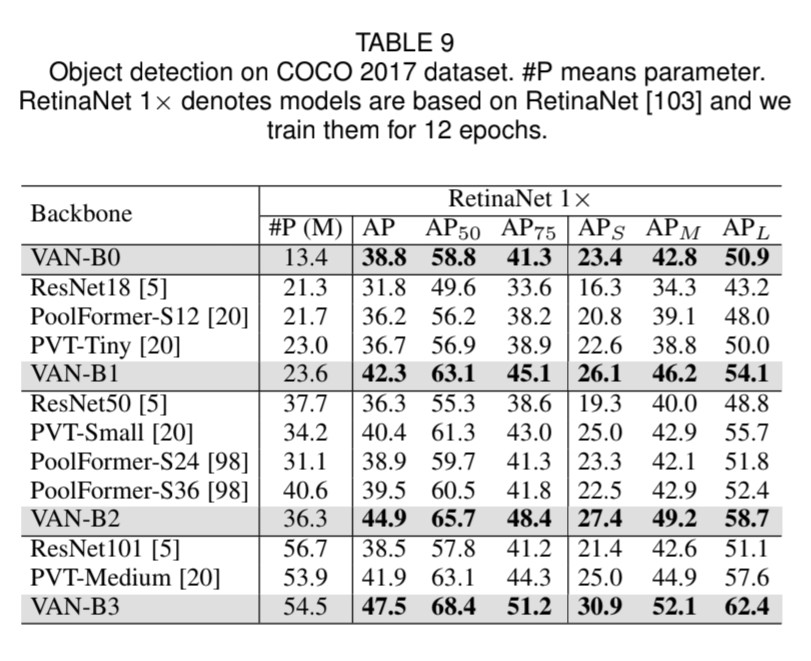
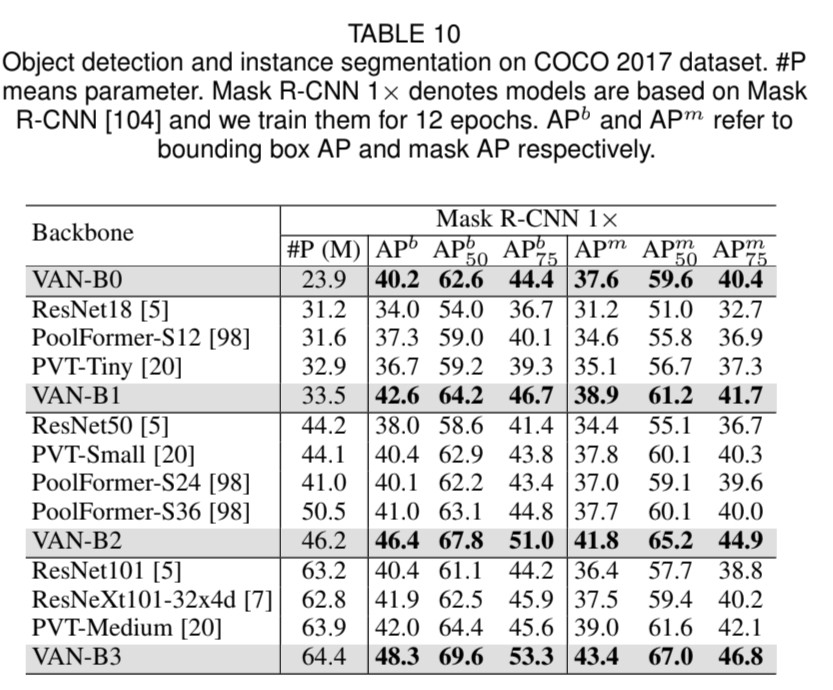
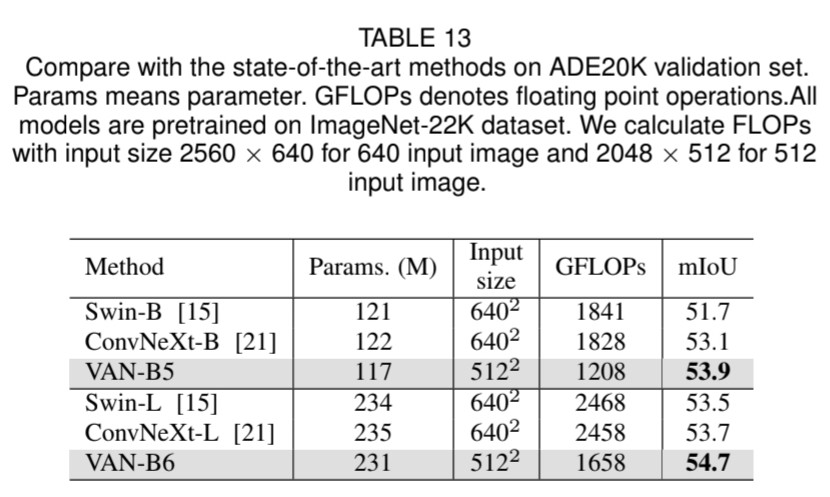
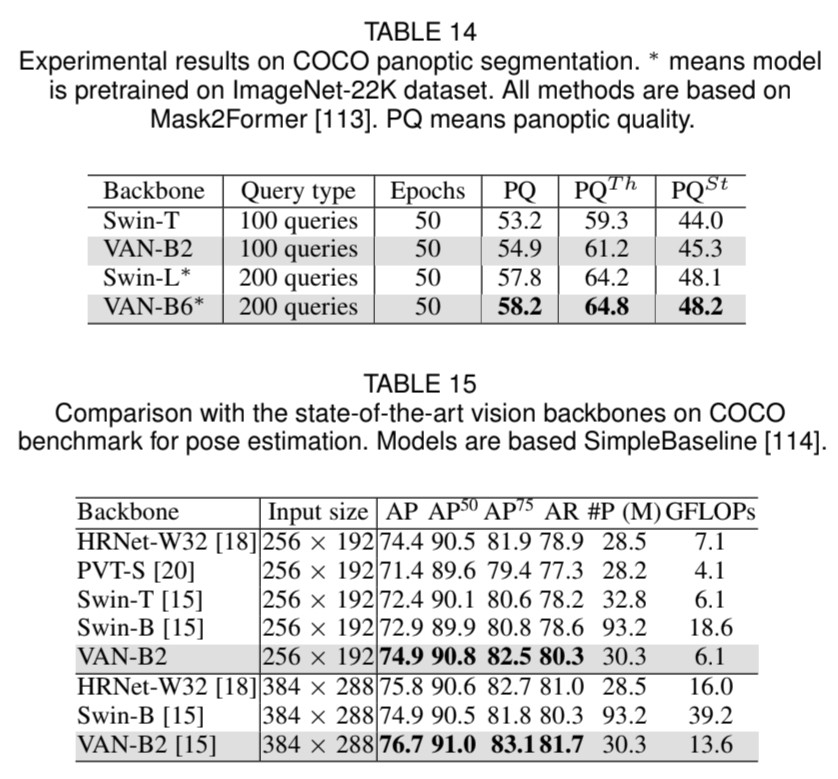
VAN의 요율성을 증명하기 위해 실험을 해보았습니다. ImageNet-1K와 ImageNet-22K을 사용하여 image classification을, COCO benchmark를 사용하여 object detection, instance segmentation, panoptic segmentation 그리고 pose estimation을, 그리고 ADE20K을 사용하여 semantic segmentation을 하였습니다. 추가로 실험 결과와 class activation mapping (CAM)을 ImageNet validation set에 Grad-CAM을 사용하여 시각화하였습니다. 실험은 Pytorch와 Jittor을 기반으로 합니다.
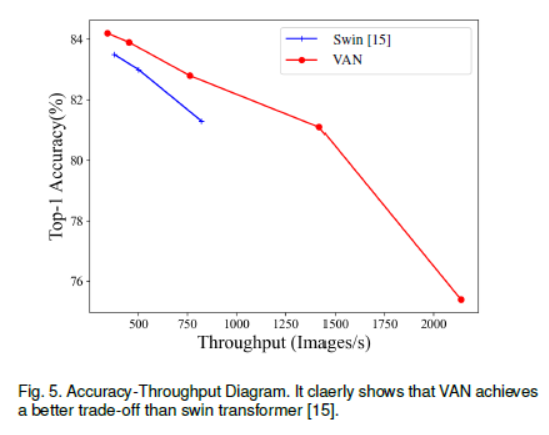
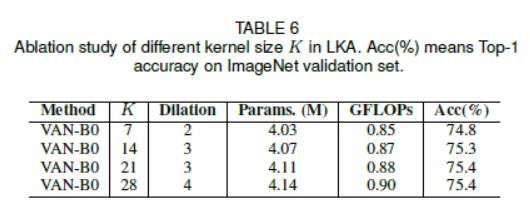
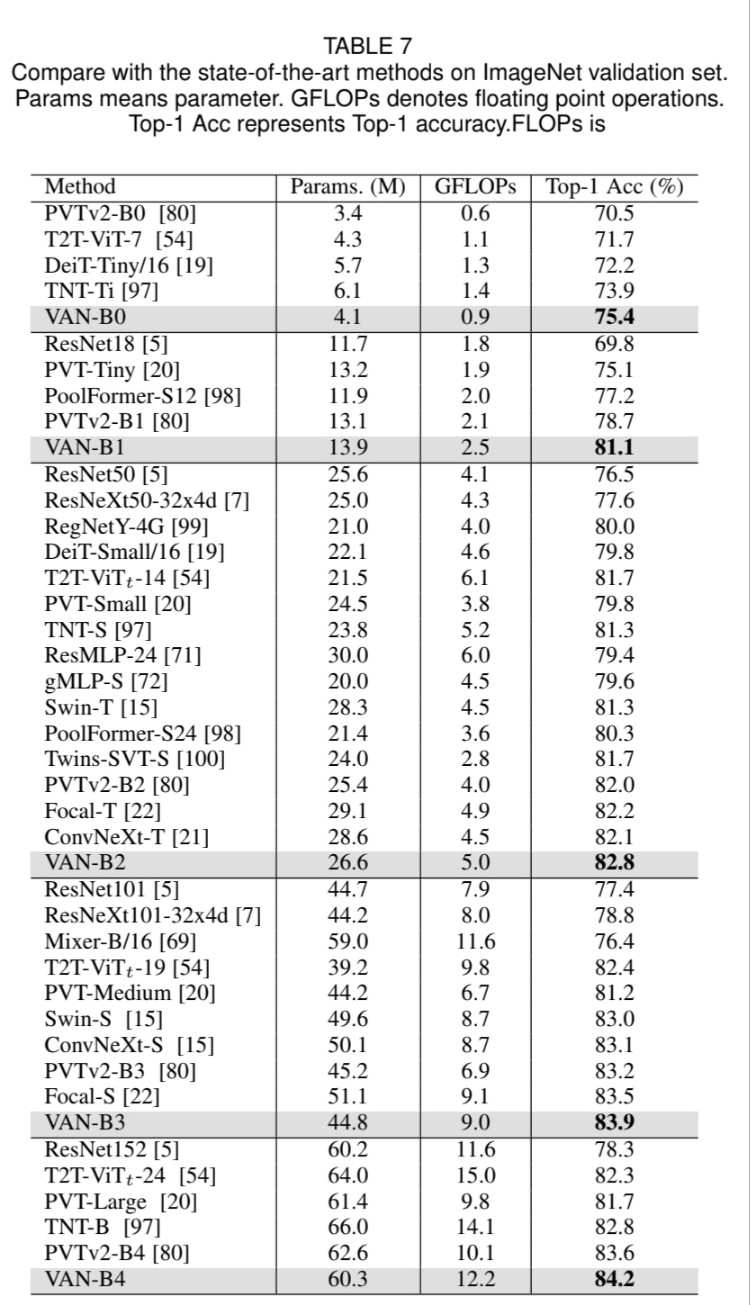
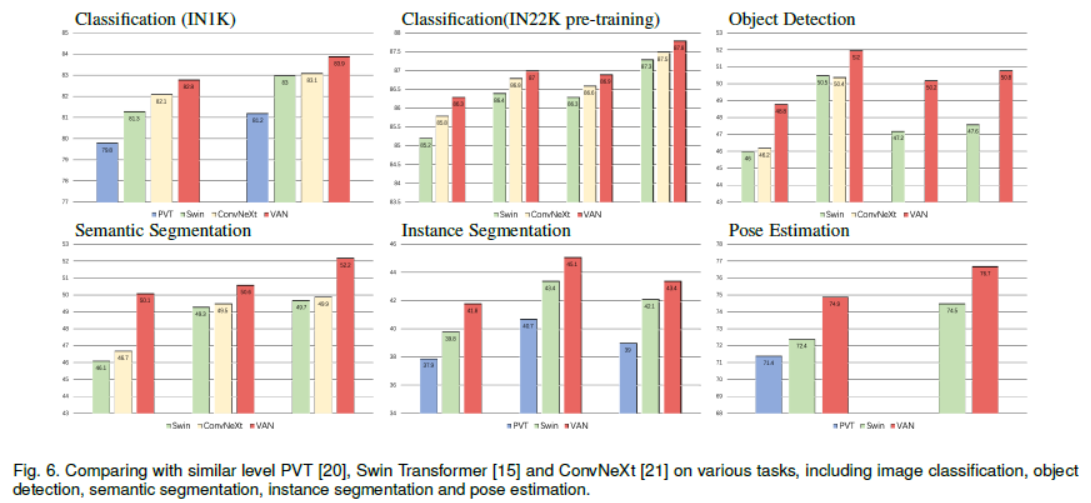
Discussion
최근에 transformer-based 모델이 다양한 vision에서 leaderboard를 정복하고 있습니다. self-attention이 특별한 attention machanism이라는 것을 알고 있습니다. 하지만, 사람들은 self-attention을 단지 default로 사용하고, attention 방법을 이해하려고 하지 않습니다. 본 논문은 새로운 attention 모듈인 LKA를 제안하고, CNN-based network인 VAN을 만들어냈습니다. 이는 vision에서 sota transformer-based 방법을 능가하죠.
추가설명
(1) spatial dimension & channel dimension
- spatial dimension은 이미지나 데이터의 폭과 높이와 같은 공간적 차원을 말함.
- channel dimension은 데이터의 깊이를 나타내며, 예를 들어 RGB 이미지는 3개의 채널로 구성됨.

Leave a comment