Attention Is All You Need
이번에는 Attention Is All You Need에 대해 논문 리뷰를 해보겠습니다. 지난 시간에 DETR을 리뷰하면서 Encoder와 Decoder에 대한 개념이 부족한 것을 느꼈습니다. 이번 기회에 Encoder와 Decoder의 개념을 파악하고 Attention이 얼마나 중요한 지를 알아보겠습니다.
배경
RNN (Recurrent Neural Network) 는 당시 language 모델링과 기계 번역과 같은 문제를 다루는 데 가장 특화된 sota 방법이었습니다.
하지만 이런 RNN은 병렬화를 못하게 하여 sequence 길이를 길게 만듭니다. 이는 메모리 사용에 치명적이며 batch을 제한하게 만들죠. 최근에는 계산 효율성을 향상시켜 모델 성능을 증가시켰지만 기본적인 sequential computation 제약은 여전했다는 것이 문제였습니다.
Attention 메커니즘은 input과 output sequence의 거리에 상관없는 sequence 모델링과 transduction 모델을 통합한 방법입니다.
본 연구는 Transformer에 대해 소개합니다. 이 모델은 recurrence, 즉 RNN 메커니즘보다 input과 output 사이의 global 의존성을 피하는 attention 메커니즘에 기반을 두고 있습니다. Transformer은 병렬화를 극대화하고, 번역의 질을 sota 수준으로 끌어올리는 데에 효과를 보여주고 있습니다.
모델 구조
Transformer는 전체적으로 stacked self-attention과 point-wise, fully connected layer를 encoder와 decoder 모두에 사용합니다.
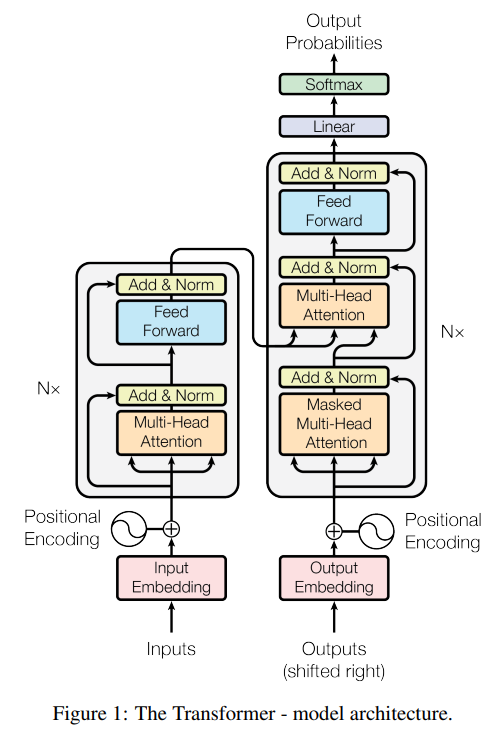
Encoder Decoder Stack
Encoder6개의 동일한 layer stack으로 구성되어 있습니다. 각 layer은 두 개의 sub layer로 구성되어 있습니다. 하나는 multi-head self-attention mechanism, 또 다른 하나는 position-wise fully connected feed-forward network입니다. 두 sub layer 주위에는 layer normalization이 residual connection으로 연결되어 있습니다. 즉 sub-layer의 output은 $\mbox{LayerNorm}(x+\mbox{Sublayer}(x))$ 가 됩니다. Residual connection을 활성화하기 위해, 모든 sub-layer은 output의 dimension을 $d_{\mbox{model}}=512$로 만듭니다.
DecoderDecoder 또한 6개의 동일한 layer stack으로 구성되어 있습니다. 하지만 encoder와 달리 decoder은 encoder stack의 output에 대하여 multi-head self-attention을 담당하는 세 번째 sub-layer가 있습니다. Encoder와 비슷하게 residual connection이 구현되어 있습니다. 한 위치가 후속 위치에 attending되는 것을 막기 위해 decoder stack에 있는 self-attention sub-layer을 수정하였습니다.
Attention
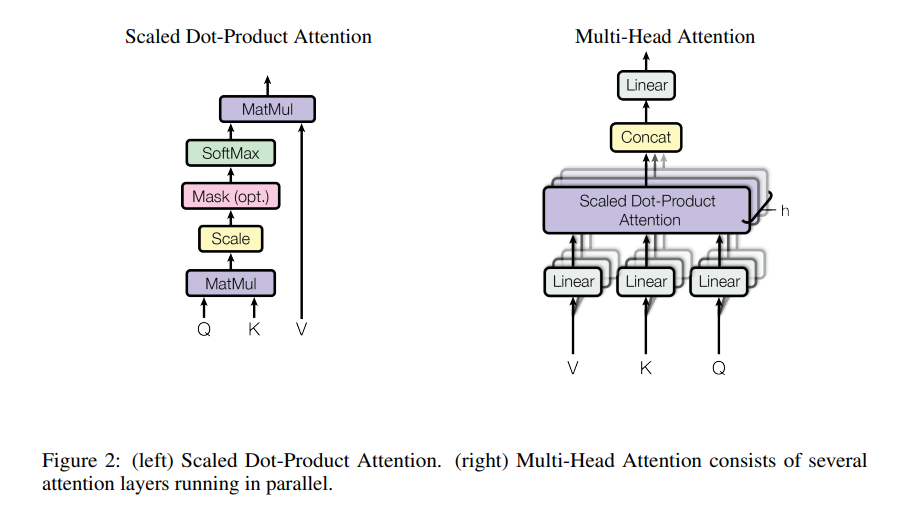
Scaled Dot-Product Attention
Scaled Dot-Product Attention이라 부르는 Attention은 queries, keys, values로 구성되어 있습니다. key의 dimension은 $\sqrt{d_k}$, valu의 dimension은 $\sqrt{d_v}$입니다.
이 Attention을 지난 output은 아래와 같이 계산됩니다.
여기서 $\frac{1}{\sqrt{d_k}}$로 곱하는 이유는 $d_k$가 크면 클수록 dot product 결과가 매우 커지기 때문에, $\sqrt{d_k}$로 나눠 gradient가 작아지는 문제를 해결하고자 했습니다.
Multi-Head Attention
$d_{\mbox{model}}$ (keys, values, queries)로 single attention function을 수행하는 것보다는, queries, keys, values를 각각 달리 학습된 linear projection에 $d_k$, $d_k$, $d_v$ dimension으로 attention을 하는 것이 효율적임을 발견하였습니다. Figure 2, 오른쪽 처럼요.

본 논문은 h=8로 설정하였으며, $d_k=d_v=d_{model}/h=64$를 사용하였습니다.
Applications of Attention in our Model
세 가지 방법으로 multi-head attention을 사용합니다.
-
“Encoder-Decoder attention” layer에 이전 decoder layer에서 queries가 오고 encoder의 output인 key와 value가 들어옵니다. 이렇게 하면 decoder의 모든 position이 input sequence에 있는 모든 position에 attend할 수 있게 됩니다.
-
Encoder은 self-attention layer를 포함하고 있습니다. self-attention layer에서는 모든 key와 value와 query는 같은 곳에서 오게 됩니다. 여기서는 아마 encoder의 이전 layer 결과값이겠네요.
-
비슷하게 Decoder에 있는 self-attention layer도 각 위치를 모든 위치에 attend 시켜줍니다.
Position-wise Feed-Forward Networks
encoder와 decoder에 있는 각 layer은 fully connected feed-forward network를 포함하고 있습니다. 사이사이에는 ReLU 활성화 함수를 포함한 linear transformation으로 구성되어 있습니다.
Embeddings and Softmax
다른 sequence transduction model과 유사하게, 본 논문은 학습된 embedding을 사용하여 input token과 output token을 dimension이 $d_{model}$인 벡터로 변환시킵니다.
Positional Encoding
본 논문의 모델은 recurrence와 convolution을 사용하지 않기 때문에, sequence의 순서를 만들어주기 위해서 상관관계와 sequence에 있는 위치 정보를 주입하였습니다. 즉, **positional encoding”을 추가하여 encoder과 decoder stack 아래 부분에 넣었습니다. positional encoding은 $d_{model}$로 같은 차원을 사용하여 같이 더해질 수 있도록 만듭니다.
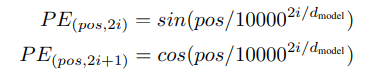
$pos$는 position을 의미하며, $i$는 dimension을 의미합니다. 위와 같이 식을 둔 이유는, 고정된 k값이라도 $\mbox{PE}_{pos+k}$ 선형 함수로 표현할 수 있어서 상대적 위치를 분석해 쉽게 학습할 수 있게 가설화하였기 때문입니다.
Self-Attention
self-attention과 recurrent and convolutional layer를 비교해보겠습니다.
self-attention은 말 그대로 attention을 자기 자신한테 취한다는 것입니다.

“The animal didn’t cross the street because it was too tired.”라는 문장이 있다면, 사람은 문맥상 it이 animal을 가리킨다는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 하지만 컴퓨터는 이해하는 과정이 매우 어렵죠. 이를 위해서 self-attention이 나오게 되었습니다.
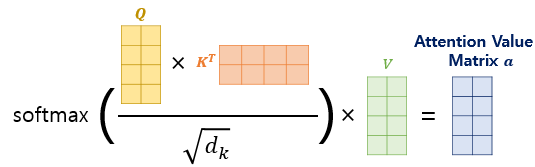
“I am a student”와 같은 문장이 있을 때, self-attention을 진행하게 되면 attention score은 아래와 같습니다.
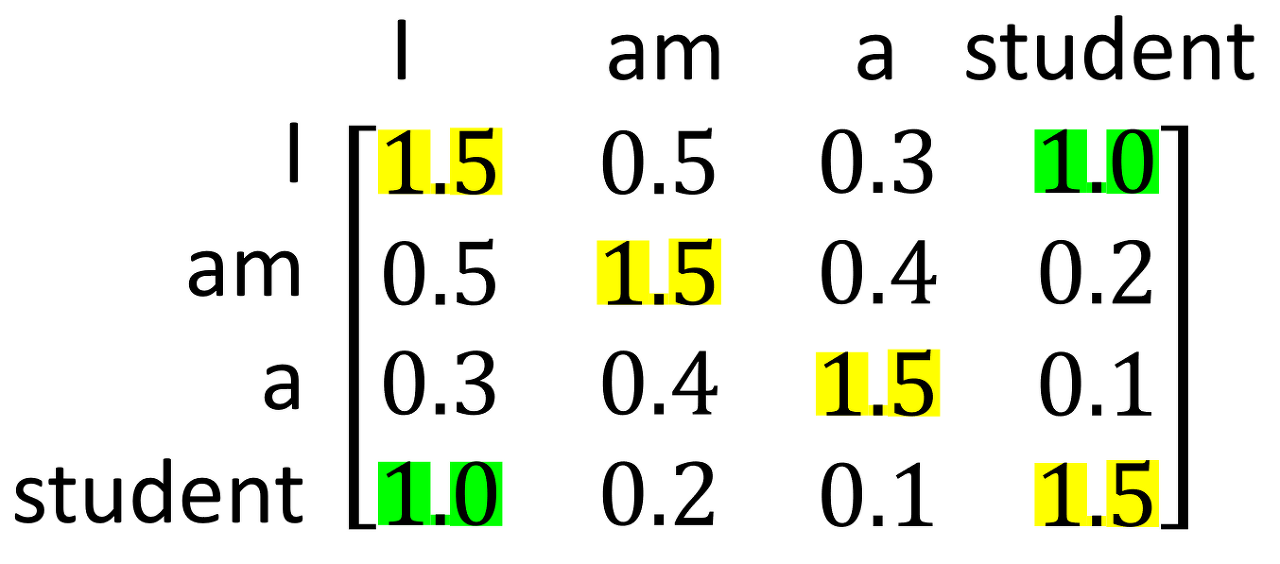
I와 student의 score가 상당히 높은 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 이 처럼 단어간의 상관관계를 recurrent나 convolution 처럼 도출할 수 있습니다. 이러한 self-attention을 적용하기 위해서는 (1) 각 층의 전체적인 계산 복잡도, (2) 병렬화할 수 있는 계산량, (3) 네트워크에 있는 long-range dependencies 사이의 path 길이를 알아야 합니다. long-range dependencies를 학습하는 것은 sequence transduction task에 주요 challenge 입니다.
long-range dependency는 long-term dependency라고도 불리는데, 과거 뉴런층의 정보가 멀리 있는 뉴런층까지 도달하기가 어렵다는 문제입니다. 이런 dependency 문제는 path 길이에 주로 영향을 받는데, 짧으면 짧을수록 long-range dependency 학습이 쉬워집니다. 이 때문에, 본 논문은 다른 층 종류로 구성된 네트워크 상에서, 두 input과 output 위치 사이의 최대 path length를 비교해보겠습니다.
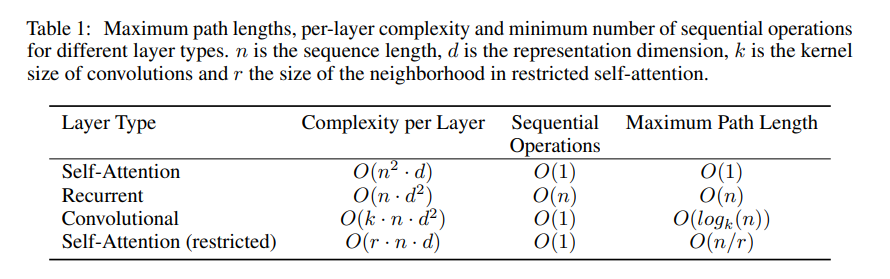
Table 1에서 보면, self-attention layer는 모든 위치를 연결하는데 일정하게 sequential operation을 수행하지만 recurrent layer은 O(n)의 sequential operation을 수행합니다. 계산 복잡도 측면에서, self-attention layer은 representation dimensionality $d$보다 더 작은 $n$을 사용하면 recurrent layer보다 빠를 수 있습니다. self-attention이 계산 복잡도나, sequential operation이나 maximum path length나 recurrent, convolution 보다 더 좋은 성능을 가지고 있네요.
실험
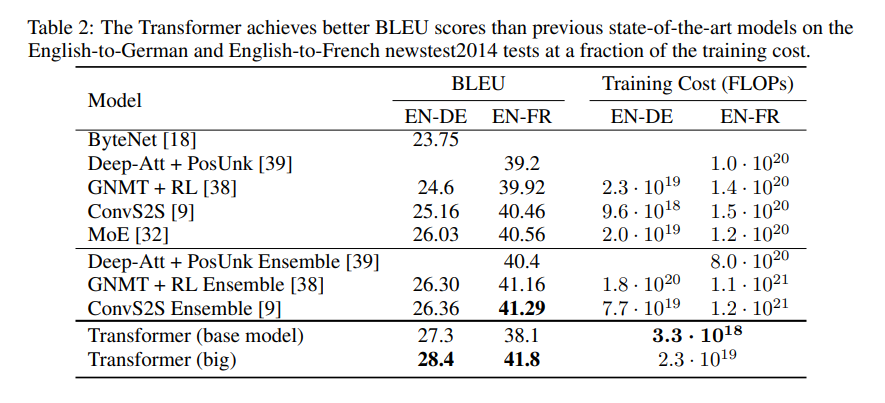
실험 결과는 위와 같습니다. BLEU 점수가 다른 Recurrent, Convolution 에 비해 높은 것을 볼 수 있으며 Training Cost, 즉 훈련 속도도 훨씬 빠른 것을 볼 수 있습니다. convolution이 아닌 self-attention base인 encode, decode로 성능을 끌어올릴 수 있네요.

Leave a comment