컴퓨터구조 공부8
Computer Architecture
우리가 항상 사용하는 컴퓨터는 정말 복잡한 시스템으로 구성되어 있다.
Parallel processor
multiple computer를 연결하여 더 높은 성능을 가지기 위해 Multiprocessor와, Scalability, availability, power efficiency를 알아야함.
Scalability는 resource에 비례해서 성능이 올라가는 지에 관련된 것임.
대부분 multiple processor (cores)로 이뤄져 있는 컴퓨터 체계임.
Hardware and Software
- Hardware
- Serial
- Parallel
- Software
- Sequential
- Concurrent
HW는 직렬, 병렬이고 SW는 순차적, 병행적임. SW는 병렬적으로 하는 것이 아닌 병행적으로 처리하기 때문에 HW가 병렬적이라고 해도 SW에서는 다를 수 있음. 항상 coefficient한 HW와 SW를 봐야함.
Parallel Programming
-
Parallel software is the problem
- Need to get significant performance improvement
- Otherwise, just use a faster uniprocessor, since it’s easier
- Difficulties
- Partitioning
- Coordination
- Communications overhead
Core를 4개 쓴다고 4배 성능이 좋아지지 않음. 그리고 여러 문제점이 있음.
Amdahl’s Law
-
Sequential part can limit speedup
-
Example : 100 processors, 90x speedup?
- $T_{new} = T_{parallelizable}/100 + T_{sequential}$
- Speedup = $\frac{1}{1-F_{parallelizable}+F_{parallelizable}/100}=90$
- Solving : $F_{parallelizable} = 0.999$
sequential part가 0.1%의 비율을 가져야 한다는 것임.
Scaling Example
- Workload: sum of 10 scalars, and 10 x 10 matrix sum
- Speed up from 10 to 100 processors
-
Single processor : $Time = (10 + 100) \times t_{add}$
- 10 processors
- Time = $10 \times t_{add} + 100/10 \times t_{add} = 20 \times t_{add}$
- Speedup = $110/20 = 5.5$ (55% of potential)
- 100 processors
- Time = $10 \times t_{add} + 100/100 \times t_{add} = 11 \times t_{add}$
- Speedup = $110/11 = 10$ (10% of potential)
resource가 많다고 linear하게 성능이 좋아지는 것은 아니나, parallel한 부분이 많으면 성능이 linear과 비슷하게 증가할 수 있음.
Instruction and Data Stream
- SISD, SIMD, MISD, MIMD가 있음
SIMD
- Operate elementwise on vectors of data
- Multiple data elements in 128-bit wide registers
- All processors execute the same instruction at the same time
- Each with different data address, etc
- Simplifies synchronization
- Reduced instruction control hardware
- Works best for highly data-parallel applications
딥러닝 가속기로 많이 쓰임
Multithreading
좋은 블로그 자료 링크
- Performing multiple threads of execution in parallel
- Replicate registers, PC, etc
- Fast switching between threads
- Fine-grain multithreading
- Switch threads after each cycle
- Interleave instruction execution
- If one thread stalls, others are executed
- Coarse-grain multithreading
- Only switch on long stall
- Simplifies hardware, but doesn’t hide short stalls
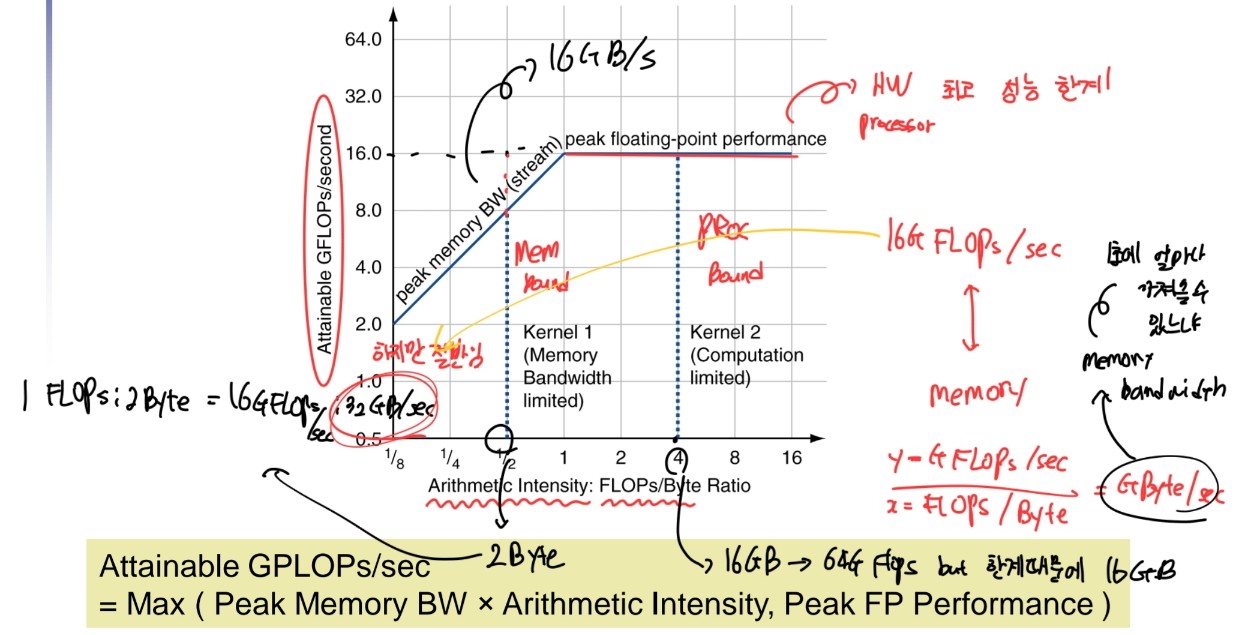
Modeling Performance
- Assume performance metric of interest is achievable GFLOPs/sec
- Measured using computational kernels from Berkeley Design Patterns
- Arithmetic intensity of a kernel
- FLOPs per byte of memory accessed
- For a given computer, determine
- Peak GFLOPS (from data sheet)
- Peak memory bytes/sec (using Stream benchmark)
FLOPS = FLOPs/sec, FLOPs = Floating Point Operations
Roofline Diagram
Optimizing Performance
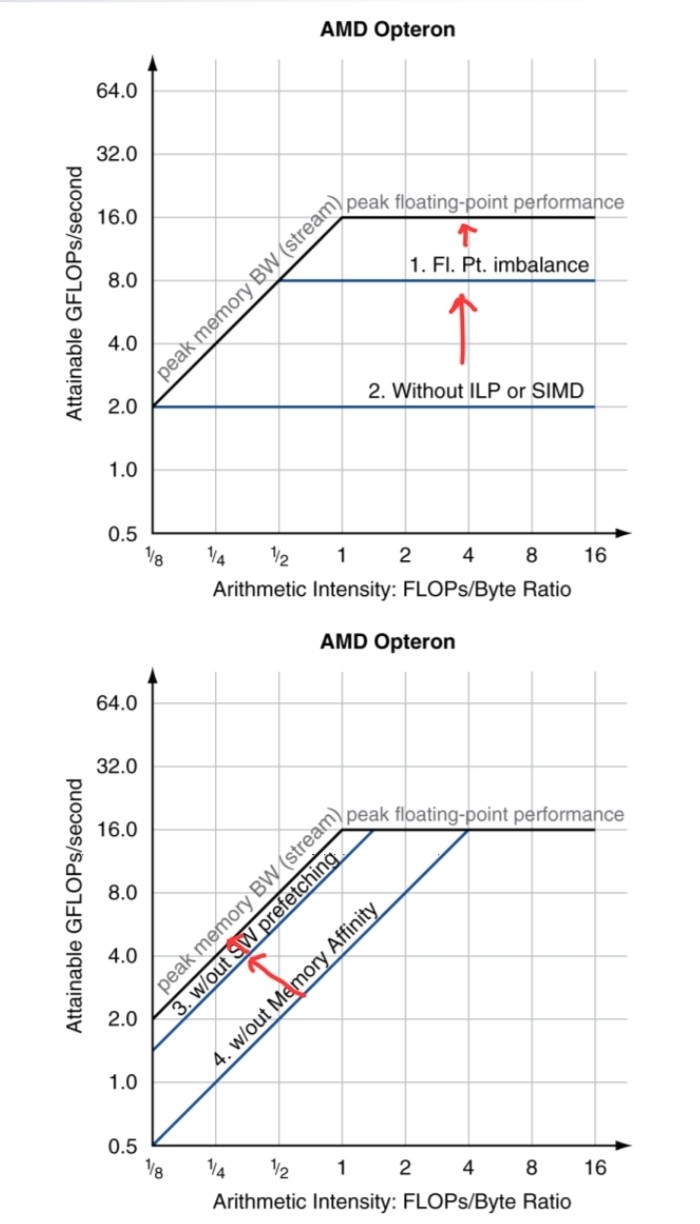
- Optimize FP performance
- Balance adds & multiplies
- Improve superscalar ILP and use of SIMD instructions
- Optimize memory usage
- Software prefetch
- Avoid load stalls
- Memory affinity
- Avoid non-local data accesses
- Software prefetch
Optimizing Performance
- Choice of optimization depends on arithmetic intensity of code
- Arithmetic intensity is not always fixed
- May scale with problem size
- Caching reduces memory accesses
- Increases arithmetic intensity

Leave a comment