컴퓨터구조 공부7
Computer Architecture
우리가 항상 사용하는 컴퓨터는 정말 복잡한 시스템으로 구성되어 있다.
Virtual Memory
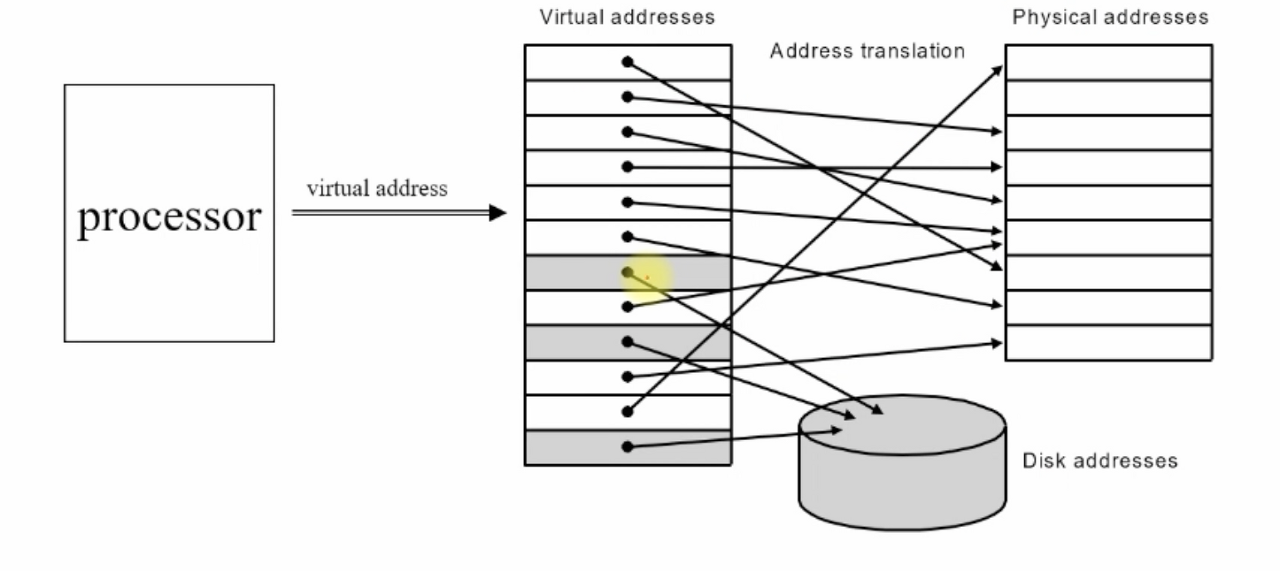
Virtual Address를 사용하여 Physical address와 Disk address를 mapping한다.
Processor는 4GB를 사용할 수 있는데, 실제 physical memory 크기는 128MB~1GB이다. (예시)
물리적 memory address는 128MB~1GB인데, virtual memory가 4GB인 것처럼 만들어준다. 위 그림 처럼 말이다.
physical memory와 disk를 mapping하여 VM은 더 큰 range를 가지게 되고 이에 processor는 큰 크기의 memory를 사용해도 되는 것처럼 보인다.
processor의 virtual address 중, physical address에 mapping되지 못한 address는 miss가 된다.
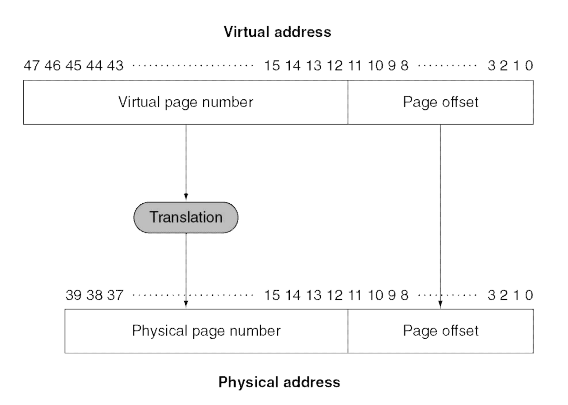
Page Tables
- Stores placement information
- Array of page table entries, indexed by virtual page number
- Page table register in CPU points to page table in physical memory
- If page is present in memory
- PTE stores the physical page number
- Plus other status bits (referenced, dirty, …)
- If page is not present
- PTE can refer to location in swap space on disk
Translation Using a Page Table
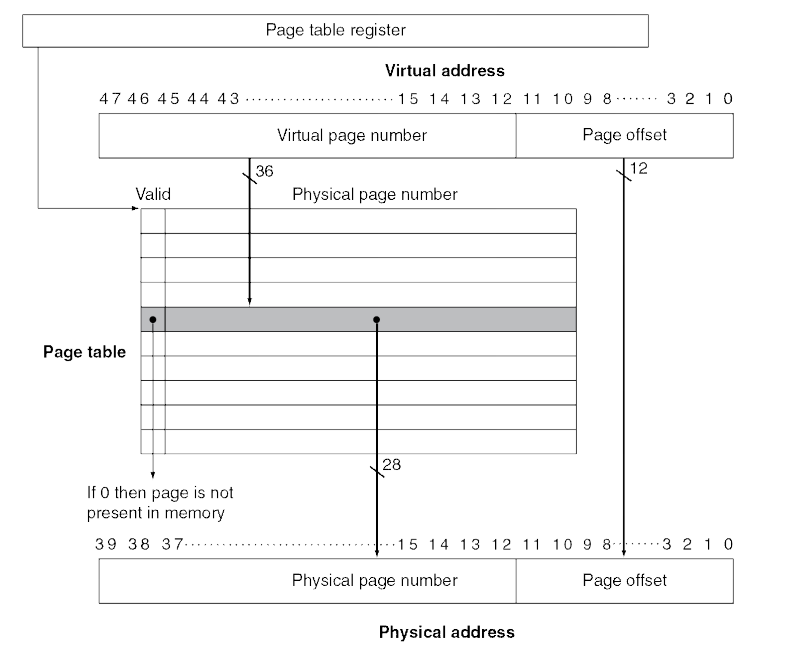
Page table을 두어서 Virtual page number를 Physical page number로 translation한다.
VPN과 PFN이 있다. VPN은 Virtual page number의 약자이고 PFN은 Physical frame number의 약자이다.
Translation Example
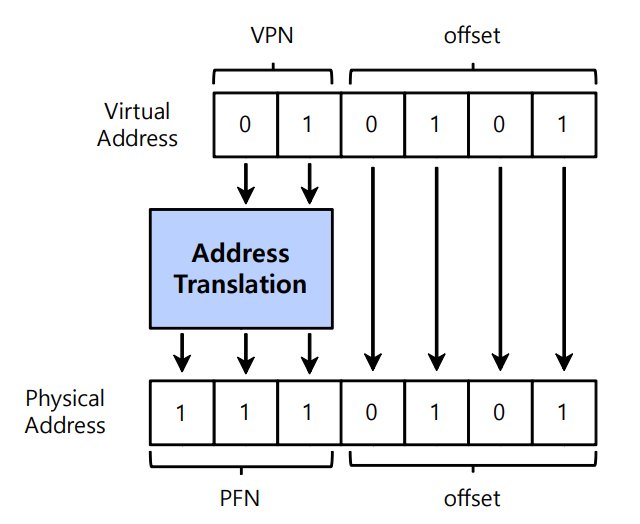
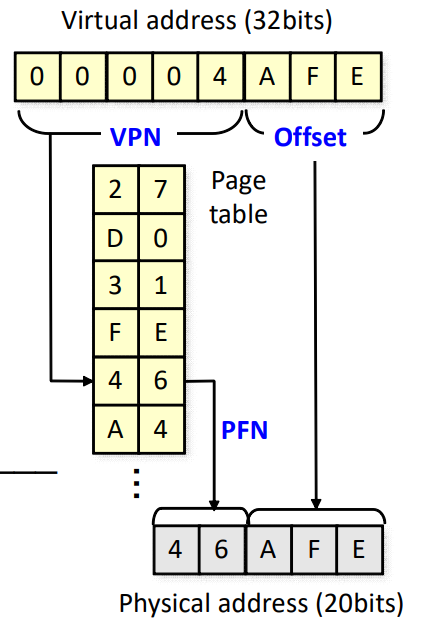
- Virtual memory space : 4GB
- Virtual address : 32 bits
- Physical memory space : 1MB
- Physical address : 20 bits
- Page size : 4KB
- Offset : 12 bits
- VPN : 20 bits, PFN : 8 bits
- Number of pages : $2^{20}$
- Number of page table entries : $2^{20}$
- Page table size : $2^{20}\times(8+8)$
Virtual Memory Performance
- Example
- Memory access time : 100ns
- Disk access time : 25ms
- Effective access time
- Let p = the probability of a page fault
- Effective access time = 100(1-p) + 25,000,000p
- If we want only 10% degradation
- 110 > 100 + 25,000,000p
- 10 > 25,000,000p
- p < 0.0000004 (one fault every 2,500,000 references)
- Page replacement 알고리즘이 성능을 좌우함. Page fault가 일어나면 안돼.
Replacement and Writes
- To reduce page fault rate, prefer least-recently used (LRU) replacement
- Reference bit in PTE set to 1 on access to page
- Periodically cleared to 0 by OS
- A page with reference bit = 0 has not been used recently
- Disk writes take millions of cycles
- Write through is impractical (Write through는 cache에 쓰여질 때 동시에 main memory에 써짐. cache coherence가 높아짐)
- Use write-back (Write back은 cache에 쓰여질 때 바로 main memory에 쓰여지지 않고, 어떤 조건에서만 쓰여짐)
- Dirty bit in PTE set when page is written
Page size
- Small page sizes
- pros : less internal fragmentation, better memory utilization
- cons : large page table, high page fault handling overheads
- Large page sizes
- pros : small page table, small page fault handling overheads
- cons : more internal fragmentation, worse memory utilization
Fast Translation Using a TLB
- Address translation would appear to require extra memory references
- One to access the PTE
- Then the actual memory access
- But access to page tables has good locality
- So use a fast cache of PTEs within the CPU
- Called a Translation Look-aside Buffer (TLB)
- Typical: 16-512 PTEs, 0.5-1 cycle for hit, 10-100 cycles for miss, 0.01%-1% miss rate
- Misses could be handled by hardware or software
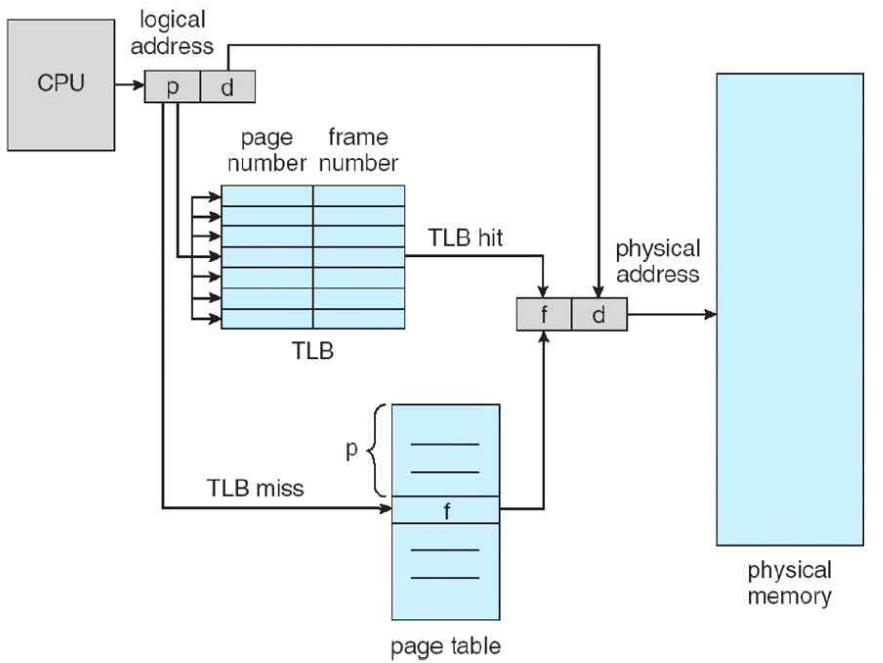
TLB Missess
- If page is in memory
- Load the PTE from memory and retry
- If page is not in memory (page fault)
- Locate page on disk
- Choose page to replace
- If dirty, write to disk first
- Read page into memory and update page table
- Then restart the faulting instruction
즉, memory에 없으면 disk에서 찾아본다는 얘기임.

Leave a comment