컴퓨터구조 공부6
Computer Architecture
우리가 항상 사용하는 컴퓨터는 정말 복잡한 시스템으로 구성되어 있다.
Memory Hierarchy
Locality
- 컴퓨터가 메모리에 한 번 접근했다면 다시 그 주소에 접근할 가능성이 크다.
- Temporal locality와 Spatial locality로 나눌 수 있다.
Temporal locality
- Items accessed recently are likely to be accessed again soon
- ex) instructions in a loop, induction variables
Spatial locality
- Items near those accessed recently are likely to be accessed soon
- ex) sequential instruction access, array data
이러한 Locality를 최대한 활용하여 Advantage를 얻어야 한다.
-> Memory Hierarchy 등장
- disk에 모든 것을 저장
- 최근에 accessed된 내용을 disk에서 더 작은 DRAM memory에 저장 (main memory)
- 그 중에서도 또 가장 최근에 accessed된 item을 더 작은 SRAM memory에 저장
- Cache memory가 CPU에 붙어있음
- Block (aka line) : unit of copying
- May be multiple words (4 bytes)
- If accessed data is present in upper level
- Hit : access satisfied by upper level
- Hit ratio : hits/accesses
- Hit : access satisfied by upper level
- If accessed data is absent
- Miss : block copied from lower level
- Time taken : miss penalty
- Miss ratio : misses/accesses = 1 - hit ratio
- Then accessed data supplied from upper level
-> Hit ratio를 높이고 Miss rate를 낮추는 것이 굉장히 중요함. Penalty를 낮출 수 있음.
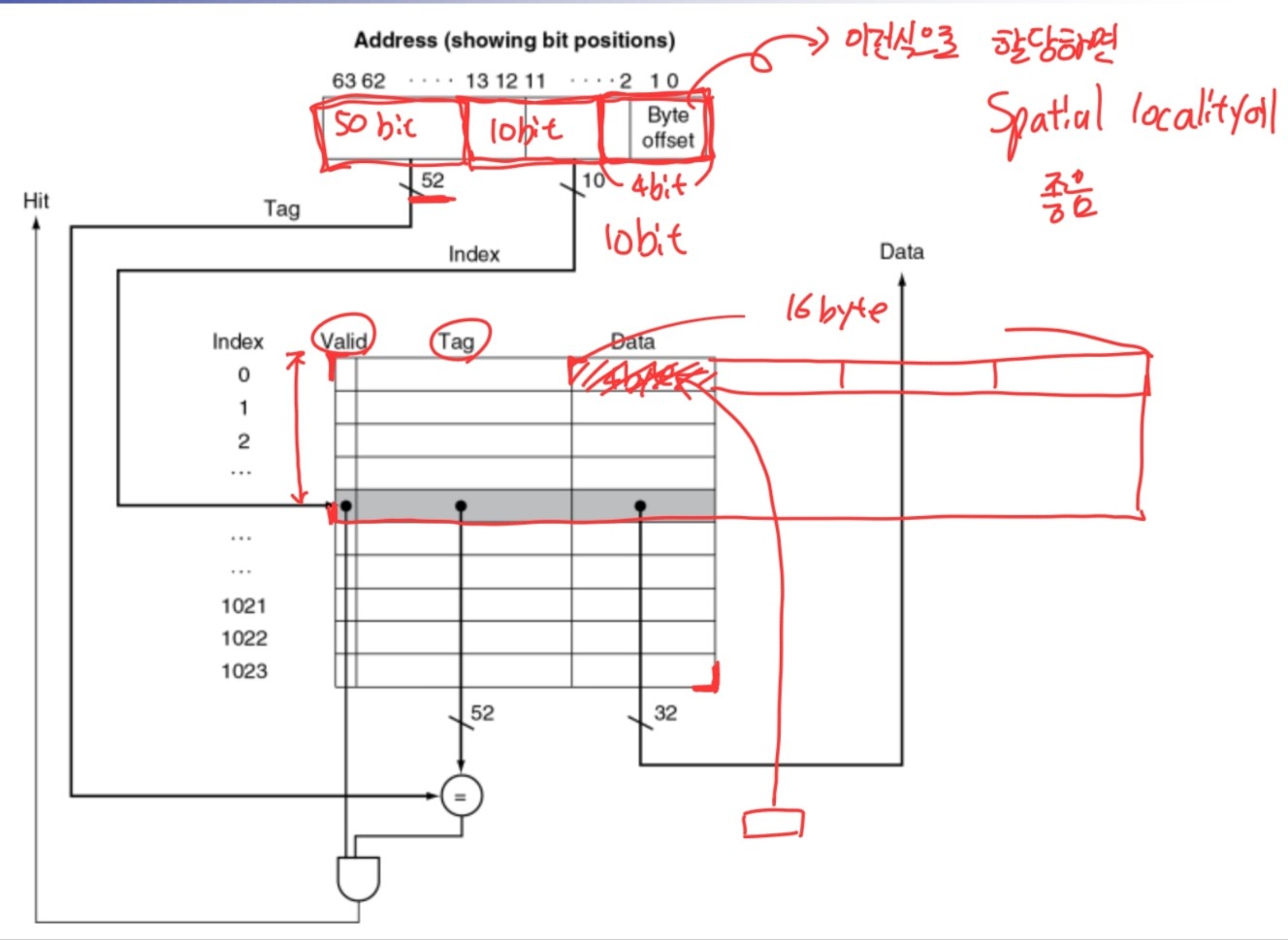
Cache Memory
- The level of the memory hierarchy closest to the CPU
- 여러가지 맵핑 방법들이 존재함
Tags and Valid Bits
- tag로 cache를 관리
- valid로 사용할 것인지 아닌지 관리
- Initially 0
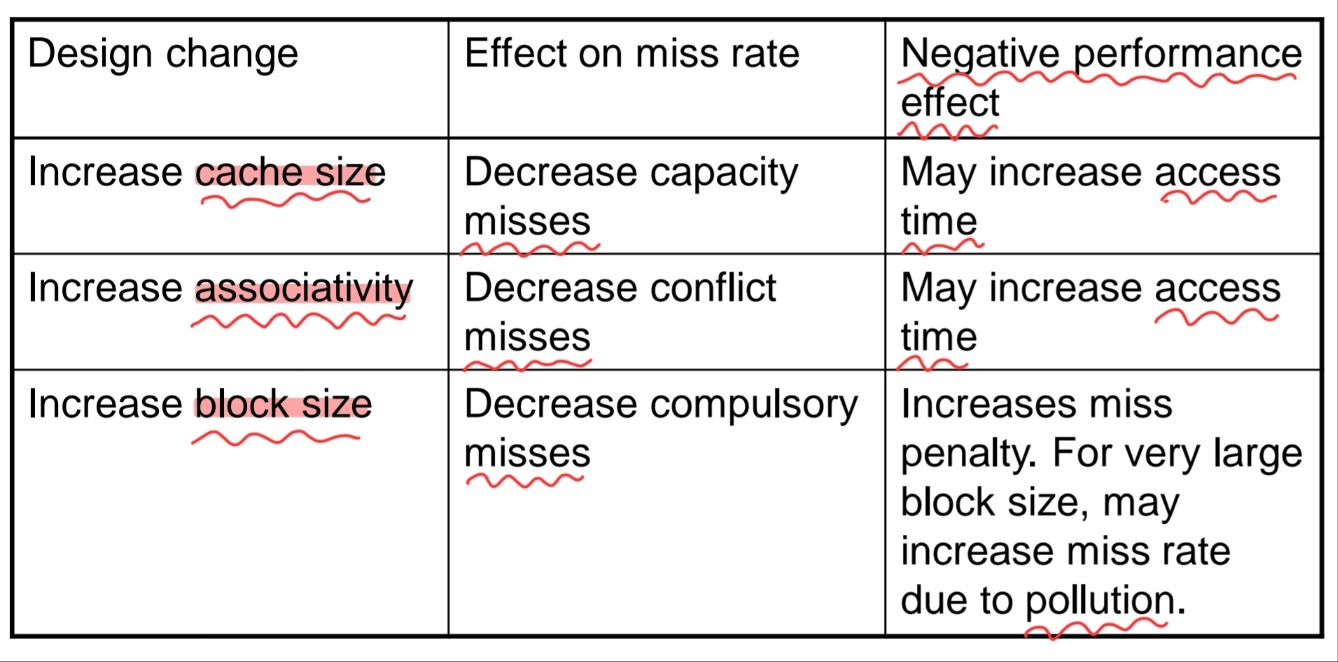
Block Size Considerations
- Larger blocks should reduce miss rate
- Due to spatial locality
- But in a fixed-sized cache
- Larger blocks -> fewer of them
- More competition -> increased miss rate
- Larger blocks -> pollution
- Larger blocks -> fewer of them
- Larger miss penalty
- Can override benefit of reduced miss rate
Cache Misses
- On cache hit, CPU proceeds normally
- On cache miss
- Stall the CPU pipeline
- Fetch block from next level of hierarchy
- Instruction cache miss
- Restart instruction fetch
- Data cache miss
- complete data access
-> cache miss 발생하지 않도록 hierarchy 개선
Write-Through
- On data-write hit, could just update the block in cache
- But then cache and memory would be inconsistent
- Write-Through : also update memory
- But makes write take longer
- Solution: write buffer
- Holds data waiting to be written to memory
- CPU continues immediately
- Only stalls on write if write buffer is already full
Write-Back
- On data-write hit, just update the block in cache
- Keep track of whether each block is dirty
- When a dirty block is replaced
- Write it back to memory
-> 즉, write-through는 memory에 즉시 업데이트, Write-Back은 dirty를 보고 memory에 업데이트
Measuring Cache Performance
$\mbox{Memory stall cycles} = \frac{\mbox{Memory accesses}}{\mbox{Program}}\times\mbox{Miss rate}\times\mbox{Miss penalty}=\frac{\mbox{Instructions}}{\mbox{Program}}\times\frac{\mbox{Misses}}{\mbox{Instruction}}\times\mbox{Miss penalty}$
Average Access Time
$\mbox{AMAT}=\mbox{Hit time}+\mbox{Miss rate}\times\mbox{Miss penalty}$
Performance Summary
- When CPU performance increased
- Miss penalty becomes more significant
- Decreasing base CPI
- Greater proportion of time spent on memory stalls
- Increasing clock rate
- Memory stalls account for more CPU cycles
- cache behavior
-> Cache behavior가 상당히 성능측에서 중요한 역할을 담당함.
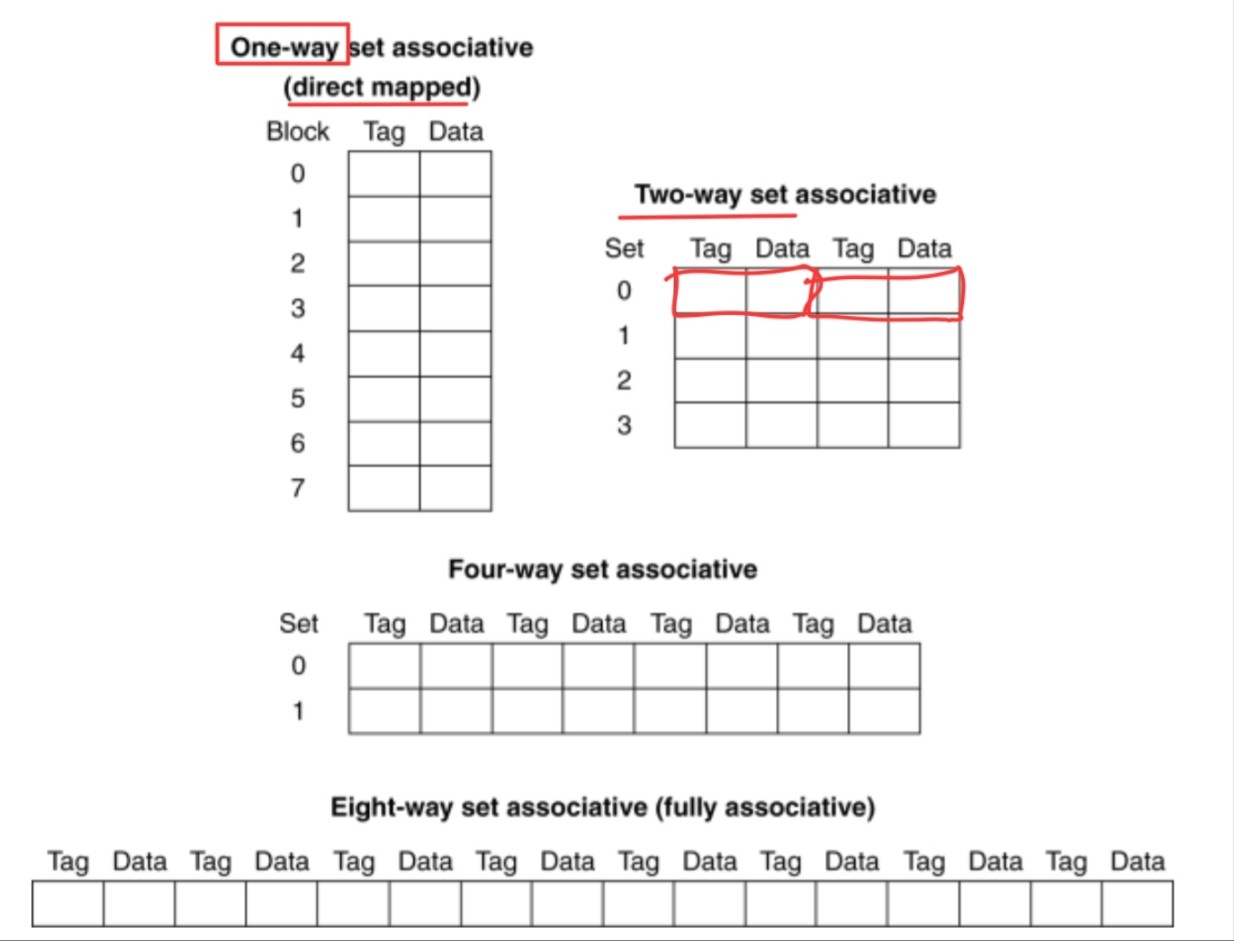
Associative Caches
- Fully associative
- Allow a given block to go in any cache entry
- Requires all entries to be searched at once
- Comparator per entry (expensive)
- n-way set associative
- Each set contains n entries
- Block number determines which set
- (Block number) modulo (#Sets in cache)
- Search all entries in a given set at once
- n comparators (less expensive)
Replacement Policy
- Direct mapped : no choice
- Set associative
- Prefer non-valid entry, if there is one
- Otherwise, choose among entries in the set
- Least-recently used (LRU)
- Choose the one unused for the longest time
- Random
- Gives approximately the same performance as LRU for high associativity
Write - allocate
- 쓰기 연산 수행할 때 cache miss 발생시, cache로 먼저 가져온 다음, cache에서 데이터를 쓰는 방식
Write - no allocate
- 쓰기 연산 수행할 때 cache miss 발생시, memory에 바로 쓰는 방식 -> memory access가 빈번하게 발생할 수 있음
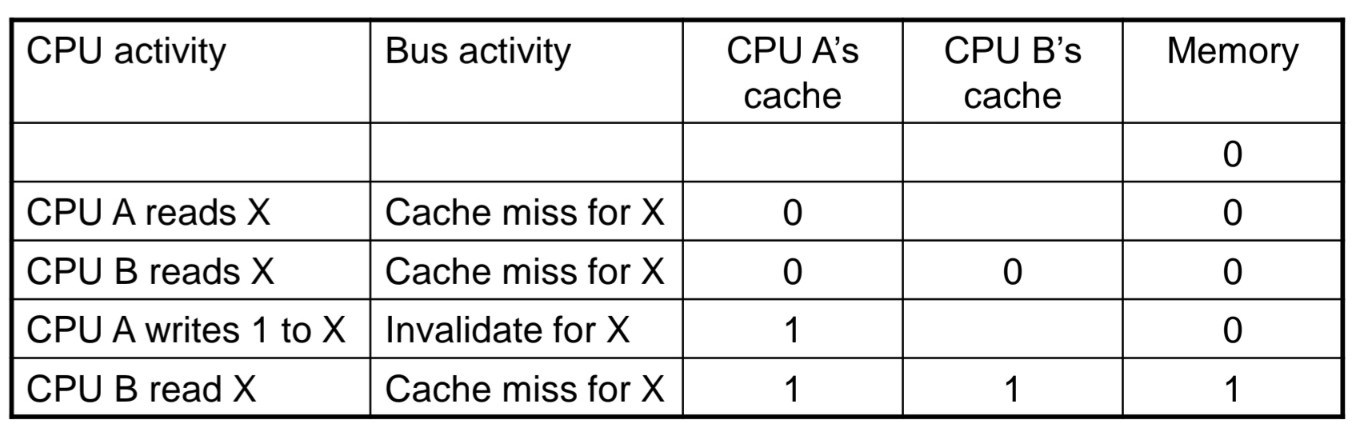
Cache Coherence Problem
- multi core 환경에서 동일한 memory 주소에 access할 시 발생함.
예시)
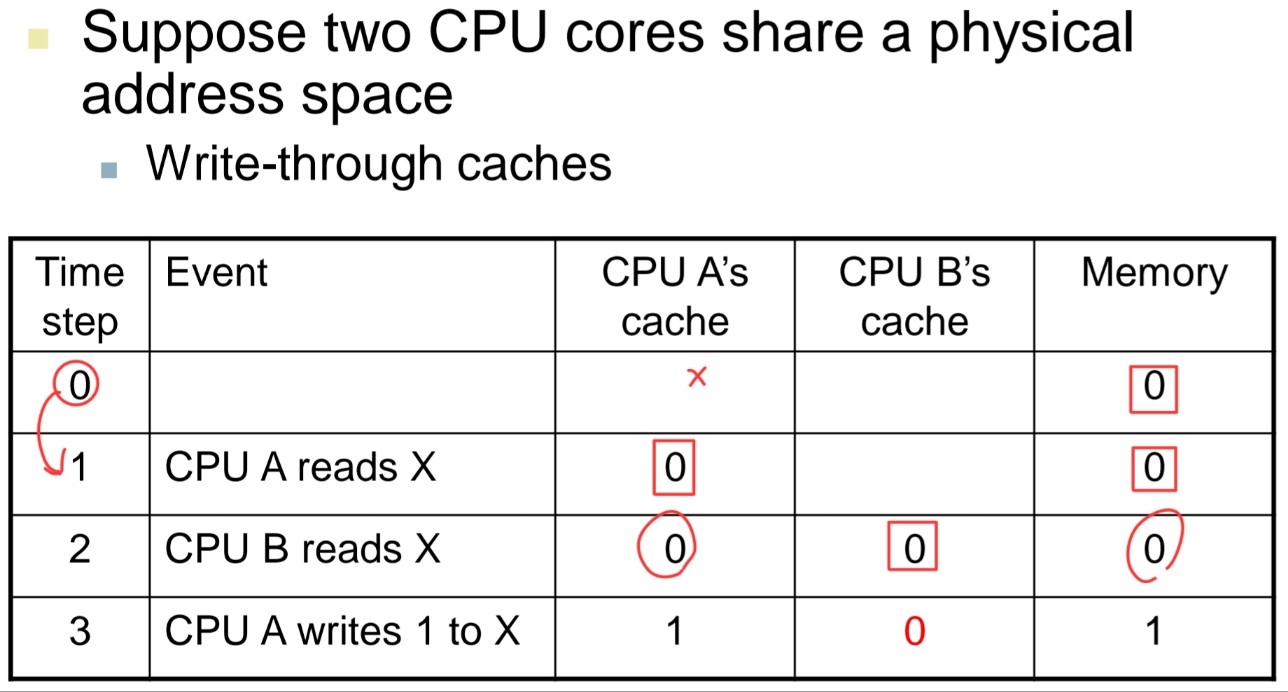
위와 같은 coherence 문제를 해결하기 위해, invalidate를 두어 coherence를 맞춰줌

Leave a comment